AnsibleでBIG-IPを操作する方法を説明します。showコマンドの出力を得たい時はbigip_commandを使用し、複数の設定を投入したい時はbigip_configを使います。その他、冪等性を担保しつつ慎重な設定を行うbigip_device_dns, bigip_hostnameなどのモジュールもあります。
BIG-IPへの接続方法
BIG-IPへの接続方法が分からない方は「Ansible操作例 – BIG-IPへの接続方法の説明」を参照ください。
このシナリオは以下のようなインベントリファイルを使用する事を前提としています。
cat << EOF > inventory.ini [bigip:vars] ansible_user = 'admin' ansible_password = 'admin' ansible_connection = 'local' [bigip] bigip161 ansible_host=192.168.1.161 bigip162 ansible_host=192.168.1.162 EOF
showコマンドの実行
プレイブック作成
以下のようなプレイブックを作成します。
着目して欲しいのはregister句です。Ansibleは実行結果を変数に格納する事ができ、その変数名を定義するのがregister句です。以下のプレイブックは、「show sys version」の実行結果を変数「result」に格納し、変数「result」をdebugで出力する例です。
cat << EOF > bigip_show_sys_version.yml
- hosts: bigip161
gather_facts: no
vars:
provider:
password: "{{ ansible_password }}"
server: "{{ ansible_host }}"
user: "{{ ansible_user }}"
validate_certs: no
tasks:
- name: run show sys version
bigip_command:
commands: show sys version
provider: "{{ provider }}"
register: result
- name: display show sys version
debug:
var: result['stdout']
EOF
戻り値の一覧
Ansibleは実行結果を変数に格納する事ができます。この実行結果をプログラミングの文脈では「戻り値」と呼ぶ事が多く、公式ドキュメントでは「Return Value」との表現を使っています。実行結果にどのような値が格納されているかは、公式ドキュメントをマニュアルを参照ください。この場合ならば、「eos command モジュール」に記載されています。
実行結果
実行結果は以下のようになります。
# ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini bigip_show_sys_version.yml
PLAY [bigip161] ****************************************************************
TASK [run show sys version] ****************************************************
ok: [bigip161]
TASK [display show sys version] ************************************************
ok: [bigip161] => {
"result['stdout']": [
"Sys::Version\nMain Package\n Product BIG-IP\n Version 16.0.0\n Build 0.0.12\n Edition Final\n Date Tue Jun 23 18:31:26 PDT 2020"
]
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
bigip161 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
複数コマンドの実行
プレイブック作成
bigip_commandは複数コマンドを同時に流し込むこともできます。以下はvlanとip addressを設定する例です。
cat << EOF > bigip_create_ipv4_address01.yml
- hosts: bigip161
gather_facts: no
vars:
provider:
password: "{{ ansible_password }}"
server: "{{ ansible_host }}"
user: "{{ ansible_user }}"
validate_certs: no
tasks:
- name: create ipv4 address
bigip_command:
commands:
- create net vlan VLAN0020 tag 20
- create net self SELF0020 vlan VLAN0020 address 10.0.20.1/24
provider: "{{ provider }}"
EOF
プレイブック実行
プレイブックを実行すると以下のように出力されます。ただし、bigip_commadsを編集用途で使用するのは非推奨であり、idempotent(冪等)ではない旨の警告が出力されます。
# ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini bigip_create_ipv4_address01.yml PLAY [bigip161] **************************************************************** TASK [create ipv4 address] ***************************************************** [WARNING]: Using "write" commands is not idempotent. You should use a module that is specifically made for that. If such a module does not exist, then please file a bug. The command in question is "create net vlan VLAN0020 tag 20..." [WARNING]: Using "write" commands is not idempotent. You should use a module that is specifically made for that. If such a module does not exist, then please file a bug. The command in question is "create net self SELF0020 vlan VLAN0020 a..." ok: [bigip161] PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************* bigip161 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
プレイブック確認
確かにプレイブックで記載された設定が投入されている事を確認します。
root@(bigip162)(cfg-sync Standalone)(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# list net vlan
net vlan VLAN0020 {
if-index 144
tag 20
}
root@(bigip162)(cfg-sync Standalone)(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# list net self
net self SELF0020 {
address 10.0.20.1/24
traffic-group traffic-group-local-only
vlan VLAN0020
}
テンプレートの利用
テンプレートの作成
Ansibleはテンプレートを作成し、そのテンプレートに記載されたconfigを流し込む事ができます。
以下にテンプレートの例を紹介します。ここで記載したテンプレートは静的なものですが、Ansibleが内部的に使うJinja2と呼ばれるテンプレートエンジンは変数読み込みや繰り返し処理も実装する事ができます。説明は省略しますが、JavaやRubyの実装経験がある人ならばJSP, ERBなどとほぼ同等機能と思って差支えございません。
cat << EOF > bigip_template.j2
net vlan VLAN0030 {
tag 30
}
net self SELF0030 {
address 10.0.30.1/24
vlan VLAN0030
}
EOF
プレイブックの作成
テンプレートを流し込むプレイブックの例を紹介します。
なお、この時に流し込む構文はtmshで指定する構文ではなく、”load sys config from-terminal merge”で指定する構文です。bigip.confやbigip_base.confで記述される構文と同じです。
cat << EOF > bigip_create_ipv4_address02.yml
- hosts: bigip161
gather_facts: no
vars:
provider:
password: "{{ ansible_password }}"
server: "{{ ansible_host }}"
user: "{{ ansible_user }}"
validate_certs: no
tasks:
- name: create ipv4 address
bigip_config:
merge_content: "{{ lookup('file', 'bigip_template.j2') }}"
provider: "{{ provider }}"
EOF
テンプレート実行
プレイブックを実行すると以下のように出力されます。
# ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini bigip_create_ipv4_address02.yml PLAY [bigip161] **************************************************************** TASK [create ipv4 address] ***************************************************** changed: [bigip161] PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************* bigip161 : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
プレイブック確認
確かにプレイブックで記載された設定が投入されている事を確認します。
root@(bigip162)(cfg-sync Standalone)(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# list net vlan
net vlan VLAN0020 {
if-index 144
tag 20
}
net vlan VLAN0030 {
if-index 160
tag 30
}
root@(bigip162)(cfg-sync Standalone)(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# list net self
net self SELF0030 {
address 10.0.30.1/24
traffic-group traffic-group-local-only
vlan VLAN0030
}
net self SELF0020 {
address 10.0.20.1/24
traffic-group traffic-group-local-only
vlan VLAN0020
}
手堅い設定投入
概要
Ansibleは、前述のbigip_command, bigip_config以外のモジュールを使用する事を推奨しています。bigip_hostname, bigip_device_dnsなどのモジュールが該当し、これらは「冪等性」が担保されたモジュールです。
「冪等性」とは「再実行しても得られる結果が同じ」という意味ですが、私個人の見解としては、「一般的な意味の冪等性」と「Ansibleの文脈での冪等性」はニュアンスが異なると理解しています。前述のbigip_configは何度実行しても「changed」と表示されますが、bigip_hostname, bigip_device_dnsなどのモジュールは設定変更が発生してない場合は「ok」のみが表示されます。Ansibleの文脈での「冪等性」とは、プレイブックを何度も実行するような運用において、changeなのかokなのかが目視チェックしやすい仕組みと理解した方が良いでしょう。
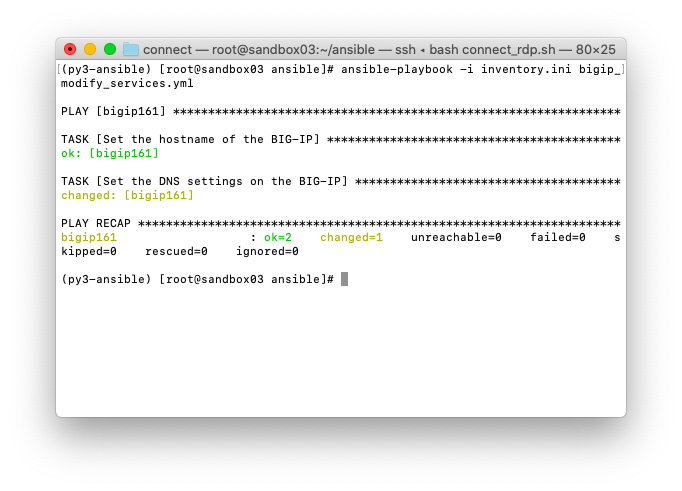
例えば、以下スクリーンショットならば、DNSは設定変更されたもののホスト名はそのままである事が一目瞭然です。
プレイブック作成
ホスト名とDNSサーバを設定する例を紹介します。
cat << EOF > bigip_modify_services.yml
---
- hosts: bigip161
gather_facts: no
vars:
provider:
password: "{{ ansible_password }}"
server: "{{ ansible_host }}"
user: "{{ ansible_user }}"
validate_certs: no
tasks:
- name: Set the hostname of the BIG-IP
bigip_hostname:
hostname: bigip162.localhost.localdomain
provider: "{{ provider }}"
- name: Set the DNS settings on the BIG-IP
bigip_device_dns:
name_servers:
- 208.67.222.222
- 208.67.220.220
search:
- localdomain
- lab.local
provider: "{{ provider }}"
EOF
プレイブック実行
プレイブックを実行すると以下のように出力されます。
# ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini bigip_modify_services.yml PLAY [bigip161] **************************************************************** TASK [Set the hostname of the BIG-IP] ****************************************** ok: [bigip161] TASK [Set the DNS settings on the BIG-IP] ************************************** ok: [bigip161] PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************* bigip161 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
プレイブック確認
確かにプレイブックで記載された設定が投入されている事を確認します。
root@(bigip162)(cfg-sync Standalone)(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# list sys global-settings hostname
sys global-settings {
hostname bigip162.localhost.localdomain
}
root@(bigip162)(cfg-sync Standalone)(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# list sys dns
sys dns {
name-servers { 208.67.222.222 208.67.220.220 }
search { localdomain lab.local }
}

